A Note On The Financial Evaluation Of Projects



 <<Previous
NET PRESENT VALUE Contd..
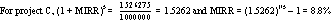
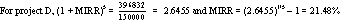
The MIRR method is superior to the IRR method. MIRR
assumes that the project cash flows are reinvested at the cost of capital
whereas the regular IRR assumes that the project cash flows are reinvested
at the project's own IRR. Since reinvestment at the cost of capital (or some
other explicit rate) is more realistic than reinvestment at IRR, MIRR
reflects the true profitability of a project. In addition, the problem of
multiple rates does not exist with MIRR. However, for choosing among
mutually exclusive projects of different size, the NPV method is better than
the MIRR method because it measures the contribution of each project to the
value of the firm.
The evaluation criteria under the MIRR method are:
•The project is accepted when the MIRR is greater than the cost of
capital or the required rate of return.
•The project is rejected when the MIRR is less than the cost of capital
or the required rate of return.
•The project reaches the point of indifference when the MIRR is equal to
the cost of capital or the required rate of return.
•When there are mutually exclusive projects, the one with the highest
MIRR must be selected. |
|
TRADITIONAL OR NON-DISCOUNTED CRITERIA
When evaluating a project's viability, traditional or non-discounted criteria generally use accounting profits rather than cash flows.
AVERAGE RATE OF RETURN METHOD
This method is also known as the accounting rate of return as it considers the accounting profits of a firm over a period of time. ARR is represented as follows:
ARR = average annual income x 100/average investment throughout the life of the project

Consider the following example:
Two machines, P and Q, with an estimated salvage value of Rs 2500 have an
initial cost of Rs 36500 and an estimated life of 5 years. Depreciation is
charged on the basis of the straight line method. The estimated income of
the machines over a period of 5 years is given in the table below. The
average rate of return of the machines is calculated as follows:
More...
APPRAISAL TECHNIQUES IN PRACTICE FOR VARIOUS TYPES OF PROJECTS
CONCLUSION
EXHIBIT I ASPECTS OF PROJECT APPRAISAL
EXHIBIT II PROJECT EVALUATION TECHNIQUES
2010, ICMR (IBS Center for Management Research).All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be
reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, used in a spreadsheet, or transmitted
in any form or by any means - electronic or mechanical, without permission.
To order copies, call +91- 8417- 236667 or write to ICMR,
Survey No. 156/157, Dontanapalli Village, Shankerpalli Mandal,
Ranga Reddy District,
Hyderabad-501504.
Andhra Pradesh, INDIA.
Mob: +91- 9640901313, Ph: +91- 8417- 236667,
Fax: +91- 8417- 236668
E-mail: info@icmrindia.org
Website: www.icmrindia.org
|