A Note On Currency And Index Futures



 <<Previous
DEFINING THE TERMS Contd..The participants in
the market are classified as hedgers, speculators and arbitrageurs. Hedgers
use futures market to reduce or eliminate the risk associated with price
fluctuations of an asset. For example, an exporter whose receivables are
denominated in another currency (say, Euro) runs a significant foreign
exchange risk, because of the possible adverse movement in the price of the
other currency vis-a-vis the home currency. The exporter can hedge the above
risk by selling futures in Euro. Speculators are those who are willing to
take the risk that the hedgers are seeking to avoid. They use futures
contracts to benefit from betting on future movements in the price of an
asset. They seek to make gains by taking long and short positions in futures
based on their own views and forecasts about the market. Arbitrageurs look
for profit from the discrepancy between prices in two different markets.
CLEARING HOUSE:
|
A clearing house is a part of the futures exchange and
acts as an intermediary in futures transactions. All futures contracts
are routed through a clearing house which is a ‘de facto'guarantor for
all futures transactions. A clearing house works closely with the
exchange but is an entity distinct from the exchange. Since all
transactions are routed through it, the clearing house becomes the buyer
to every seller and seller to every buyer. Let us understand the process
with the help of following illustration:
There are two parties, A and B, who want to enter into a futures
contract. A typical transaction with, and without, the involvement of a
clearing house would be as follows: |
|
In the first case, where the transaction
takes place without the clearing house both A and B assume the counterparty
risk[5] because on the date of the contract, B may fail to deliver the
underlying asset or A may fail to pay the price. In the second case, the
clearing house replaces B as a seller to A, and A as a buyer to B, and thus
the credit risk taken by both A and B becomes insignificant. FIGURE I
TRANSACTION WITHOUT CLEARING HOUSE



 
TRANSACTION INVOLVING CLEARING HOUSE




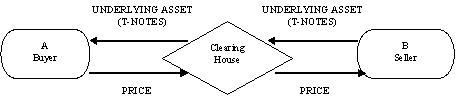
The clearing house assumes many important functions like ensuring smooth trading by maintaining delivery schedules, minimizing credit risk by becoming counterparty to every transaction, monitoring speculation margins and more. Since the clearing house undertakes counterparty risk for all transactions, the total risk assumed by it is high. Thus, it becomes important for the clearing house to minimize this risk, which is done by collecting margins. Margins are levied for all transactions depending on the volatility of the underlying asset, and adjustment is done everyday depending upon the prices, a process known as marking to market.
TYPES OF MARGIN:
SETTLEMENT PROCEDURES
APPLICATIONS OF FUTURES
TYPES OF FUTURES
TRADING USING CURRENCY FUTURES
TRADING USING INDEX FUTURES
CONCLUSION
EXHIBIT I DIFFERENCE BETWEEN FUTURES AND FORWARDS CONTRACTS
EXHIBIT II A NOTE ON ANALYZING FUTURES PRICES
ADDITIONAL READINGS AND REFERENCES
[5] The risk to each party of a contract that the counterparty will not live
up to its contractual obligations.
2010, ICMR (IBS Center for Management Research).All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be
reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, used in a spreadsheet, or transmitted
in any form or by any means - electronic or mechanical, without permission.
To order copies, call +91- 8417- 236667 or write to ICMR,
Survey No. 156/157, Dontanapalli Village, Shankerpalli Mandal,
Ranga Reddy District,
Hyderabad-501504.
Andhra Pradesh, INDIA.
Mob: +91- 9640901313, Ph: +91- 8417- 236667,
Fax: +91- 8417- 236668
E-mail: info@icmrindia.org
Website: www.icmrindia.org
|