A Note On Investment Strategies Involving Options



 <<Previous
INVESTMENT STRATEGIES INVOLVING OPTIONS Contd..
Condor Spread
A condor spread trading strategy involves the use of four options with the
same expiration date. A condor spread is similar to a butterfly spread, the
only difference being that unlike the latter, all the four options in it
have different exercise prices. To create a condor spread two options are to
be bought at the extreme exercise prices and two are sold at two different
halfway prices. Both the upside potential and the downside risk in this
strategy are limited.
Example:
A buys two March call options on shares of Andhra Bank, one
at a premium of Rs. 8 per share with a strike price of Rs.40 (X1) and the other
at a premium of Rs. 2 per share with a strike price of Rs. 74 (X4). A also sells
two March call options one at a premium of Rs. 5 per share with a strike price
of Rs. 50 (X2) and the other at a premium of Rs. 3 per share with a strike price
of Rs. 64 (X3). The payoff table (Refer Table 9) of a long condor spread will
be: Table 9: Payoff using Condor Spread
 | | | |




| S
|
X1
|
X2
|
X3
|
X4
|
C
|
Payoff
|
Net Profit |
| 36
|
40
|
50
|
64
|
74
|
2
|
0
|
-2 |
| 40
|
40
|
50
|
64
|
74
|
2
|
0
|
-2 |
| 44
|
40
|
50
|
64
|
74
|
2
|
4
|
2 |
| 48
|
40
|
50
|
64
|
74
|
2
|
8
|
6 |
| 50
|
40
|
50
|
64
|
74
|
2
|
10
|
8 |
| 54
|
40
|
50
|
64
|
74
|
2
|
10
|
8 |
| 58
|
40
|
50
|
64
|
74
|
2
|
10
|
8 |
| 62
|
40
|
50
|
64
|
74
|
2
|
10
|
8 |
| 64
|
40
|
50
|
64
|
74
|
2
|
10
|
8 |
| 68
|
40
|
50
|
64
|
74
|
2
|
6
|
4 |
| 72
|
40
|
50
|
64
|
74
|
2
|
2
|
0 |
| 74
|
40
|
50
|
64
|
74
|
2
|
0
|
-2 |
| 78
|
40
|
50
|
64
|
74
|
2
|
0
|
-2 |
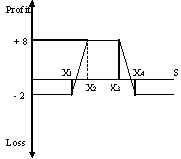
In a calendar spread, options have the same exercise price but different expiration dates. A long calendar spread can be created by using call or put options. In this case, an investor buys a call or put option with a long-term maturity with a certain exercise price and sells a short-term maturity call or put option at the same exercise price. A long calendar spread requires an initial investment, as longer the term of maturity of an option, the more valuable it is. A calendar spread is so designed to take advantage of the time decay, wherein the option closer to maturity loses its value at a much greater rate as it approaches the expiration date than the option with a longer term to maturity. This is because options closer to maturity are more volatile than an option with a long term for maturity. A short calendar spread also known as the reverse calendar spread is the opposite of the long calendar spread. Here, an investor buys a short maturity option and sells a long maturity option.
More...
TABLE 10: PAYOFF FROM LONG STRADDLE
TABLE 11: PAYOFF FROM LONG STRANGLE
TABLE 12: PAYOFF USING STRIPS
TABLE 13: PAYOFF USING STRAP
CONCLUSION
EXHIBIT I
ADDITIONAL READING & REFERENCES
2010, ICMR (IBS Center for Management Research).All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be
reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, used in a spreadsheet, or transmitted
in any form or by any means - electronic or mechanical, without permission.
To order copies, call +91- 8417- 236667 or write to ICMR,
Survey No. 156/157, Dontanapalli Village, Shankerpalli Mandal,
Ranga Reddy District,
Hyderabad-501504.
Andhra Pradesh, INDIA.
Mob: +91- 9640901313, Ph: +91- 8417- 236667,
Fax: +91- 8417- 236668
E-mail: info@icmrindia.org
Website: www.icmrindia.org
|