Enterprise Risk Management at ABN AMRO




<<Previous
Risk Governance
|
The Managing Board established the risk philosophy and policies for ABN AMRO
under the guidance of the Supervisory Board. Responsibility for the overall
implementation of risk policy lay with the Chief Financial Officer, who was a
member of the Managing Board. Risk was managed through two principal
departments: Group Risk Management (GRM) and Group Asset and Liability
Management (GALM).
GRM was responsible for the management of credit, country, market and
operational risks and was also responsible for leading the assessment of
the impact of the New Capital Accord (Basel II) and its implementation.
GALM attempted to protected the earnings and capital position of the
bank from adverse interest rate and currency movements. GALM also
managed the group's longer-term liquidity profile. Overnight liquidity
or cash management was taken care of by the Treasury department in WCS
(Wholesale Client Services).
|
|
Exhibit: III
ABN AMRO: Risk Governance Organizational




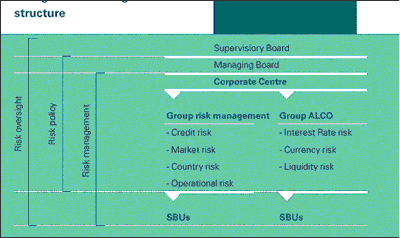
Source: ABN AMRO Annual Report, 2002.
Group Risk Management
The Group Risk Committee (GRC) was the highest-ranking committee on policy
and exposure approval for credit, country and market risk.
GRC's main responsibilities were to:
• Determine the risk policies, procedures and methodologies for measuring and
monitoring risk
• Set delegated credit authorities for lower committees and authorized
individuals within GRM, C&CC (Consumer and Commercial Clients) and PC&AM
(Private Clients and Asset Management)
• Approve credit, market and operational risk associated with new products
• Approve risk transactions larger than the delegated authorities of lower
committees
• Set the overall value-at-risk (VAR) for the bank's trading products globally
• Oversee the bank's overall portfolio for WCS, C&CC and PC&AM.
Exhibit: IV
ABN AMRO: Consumer & Commercial Clients




|
(in millions) |
2002 |
2001 |
2000 |
|
Net interest revenue |
6,853 |
6,812 |
6,970 |
|
Net commissions |
1,658 |
1,852 |
1,988 |
|
Results from financial transactions |
226 |
272 |
266 |
|
Other revenue |
1,645 |
1,267 |
802 |
|
Total revenue |
10,382 |
10,203 |
10,026 |
|
Operating expenses |
6,710 |
7,052 |
6,809 |
|
Operating result |
3,672 |
3,151 |
3,217 |
|
Provisioning for loan losses |
881 |
802 |
612 |
|
Value adjustments to financial fixed assets |
8 |
2 |
|
|
Operating profit before taxes |
2,783 |
2,347 |
2,605 |
|
Taxes |
744 |
584 |
700 |
|
Minority interests |
21 |
99 |
129 |
|
Net profit |
2,018 |
1,664 |
1,776 |
|
Total assets |
229,181 |
242,796 |
223,154 |
|
Risk-weighted assets |
143,449 |
158,141 |
157,385 |
|
Full-time equivalent staff |
71,340 |
73,736 |
75,867 |
|
Number of branches and offices |
3,078 |
3,161 |
3,238 |
Source: ABN AMRO Annual Report, 2002
The credit risk organizations of C&CC and PC&AM had a local
focus and were overseen by GRM. The WCS risk function had been integrated into
GRM. Market risk and operational risk were separate risk functions within GRM.
Country risk officers were part of GRM and provided local oversight.
The main responsibilities of C&CC, PC&AM and GRM were:
• Overseeing all credit, market and regulatory matters and ensuring compliance
with local laws
• Approving risk transactions within delegated limits or advising on credits,
which exceeded such authority
• Implementing review and control policies on all risk portfolios
• Establishing and maintaining operational risk control discipline
• Ensuring compliance with the bank's Values and Business Principles.
Basel Framework and Status
In January 2001, the Basel Committee on Banking Supervision (BCBS) published
its second Consultative Document reviewing the Basel Accord of 1988. The
European Commission also published a new draft Directive. In 2002, the BCBS
delayed publication of the New Capital Accord to the end of 2003, simultaneously
delaying its implementation until 2006.
The BCBS launched its third Quantitative Impact Survey (QIS3) in October 2002,
which incorporated potential changes to the second Consultative Document, in
line with some industry recommendations. The BCBS was expected to finalize the
Accord partly on the basis of the results of QIS3. ABN AMRO participated in the
survey as part of its close involvement in the consultations on the New Capital
Accord.
ABN AMRO supported the increased risk-sensitive nature of the proposed New
Capital Accord. The resulting regulatory framework was much more detailed and
complex. ABN Amro believed there was a need for balance between the appropriate
risk sensitivity, a level international playing field and the regulatory burden.
The bank had set up a project group to work on the implementation of the coming
capital adequacy regulations on an Internal Rating Based basis for credit risk
and Advanced Measurement Approach for operational risk.
More >>
©2003, . All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, used in a spreadsheet, or transmitted in any form or by any means - electronic or mechanical, without permission.
To order copies, call 0091-40-2343-0462/63 or write to ICMR,
Survey No. 156/157, Dontanapalli Village, Shankerpalli Mandal,
Ranga Reddy District,
Hyderabad-501504.
Andhra Pradesh, INDIA.
Mob: +91- 9640901313, Ph: +91- 8417- 236667,
Fax: +91- 8417- 236668
E-mail: info@icmrindia.org
Website: www.icmrindia.org
|